Back To The Indian History Master Index
Post Mauryan Period
- Shunga Dynasty (185–72 BC)
- Kanva Dynasty (73–26 BC)
- Sakas in the North Western India 90BC
- Kushan Dynasty (100-200AD)
- The world map during Kushan Dynasty
- Kanishka (78-101 AD)
- The Western Satraps (35-405 AD, The Kshatrapas or The Sakas, rulers of Malwa, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Rajasthan.)
Sunga dynasty 185-72 BC

Pushyamitra Shunga (185–149 BCE) was the founder and first ruler of the Shunga Empire in North India. Pushyamitra was originally a Senapati “General” of the Maurya Empire. In 185 BCE he assassinated the last Mauryan Emperor, Brihadratha Maurya. Devabhuti (r. 83 – 73 BC) was the last king of the Shunga Empire. He was assassinated by his minister Vasudeva Kanva and is said to have been overfond of the company of women. Following his death, the Shunga dynasty was then replaced by the Kanvas.
Kanva Kings
Vasudeva (c. 75 – c. 66 BCE)
Bhumimitra (c. 66 – c. 52 BCE)
Narayana (c. 52 – c. 40 BCE)
Susharman (c. 40 – c. 30 BCE)
Vasudeva Kanva (75–66 BCE) was the founder of the Kanva dynasty. He was originally an Amatya (minister) of last Shunga ruler Devabhuti. Bana’s Harshacharita informs us that he came to power after the death of Devabhuti Magadha was ruled by four Kanva rulers. Their dynasty was brought to an end by the ruler of the Satavahana dynasty or Andhrabhrtya dynasty in Amaravathi village, Guntur district.. He was succeeded by his son Bhumimitra.
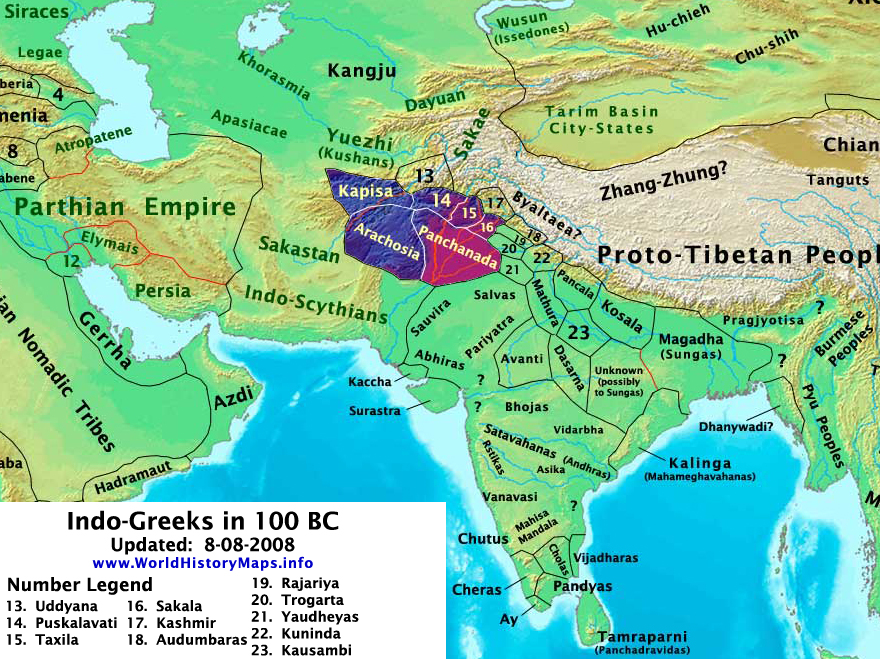
The Sakas or Indo-Scythes
Venue: North West India
Year: 90 BC onwards Yuezhi, Wade-Giles romanization Yüeh-chih, also called Indo-Scyth or Sakas, ancient people who ruled in Bactria and India from about 127-151AD. Ancient Bactria was located between the Hindu Kush mountain range and the Amu Darya river, covering the flat region that straddles modern-day Afghanistan and Tajikistan.

The map above shows the migration of Yuezhi people into India.
The Sakas Invaded India and bring five areas under their dominion as shown above: Taxila (Capital) in Punjab, Gandhara in Afganistan, Mathura, Sakastan in Western India and Ujjayini in Upper Deccan. The Lower Deccan was ruled by Satabahana Kings.

Kushan Dynasty 30–375


| King | Length of Reign | Dates of Inscriptions |
| Kajula Kadphises | min.23 years | 103-136 |
| Vima Kadphises | 184(7) | |
| Kanishka (78-101 AD) | 23 years | 1-23 |
| Huvishka | 32-40 years | 28-60 |
| Vasudeva | 34-40 years | 64-98 |
| Kanishka II | aprox.19 years | |
| Vasishka | 8 – 20 years | 20-28 |
| Kanishka III | unknown | 41 |
| Vasudeva II | unknown | 170 (disputed) |
| Shaka | unknown |
The Kushana Empire was established in ancient India by Kujala Kadphises. He was succeeded by his son Vima Kadphises, who consolidated a strong Kushana Empire in India. It spread to encompass much of Afghanistan, today’s Peshawar, Pakistan, and then the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath near Varanasi (Benares), where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great.
Kanishka, Mathura Museum.
Kaniska reign began in 100 AD. Under him, the Kushan kingdom reached its height. It was acknowledged as one of the four great Eurasian powers of its time (the others being China, Rome, and Parthia). Kanishka had a winter capital at Purushapura (Peshawar, Afghanistan) and a summer capital at Kapisa (Bagram). His kingdom extended from Bukhara in the west to Patna in the Ganges Valley in the east, from the Pamirs in the north to central India in the south.The Kushans were instrumental in spreading Buddhism in Central Asia and China and in developing Mahayana Buddhism and the Gandhara and Mathura schools of art.
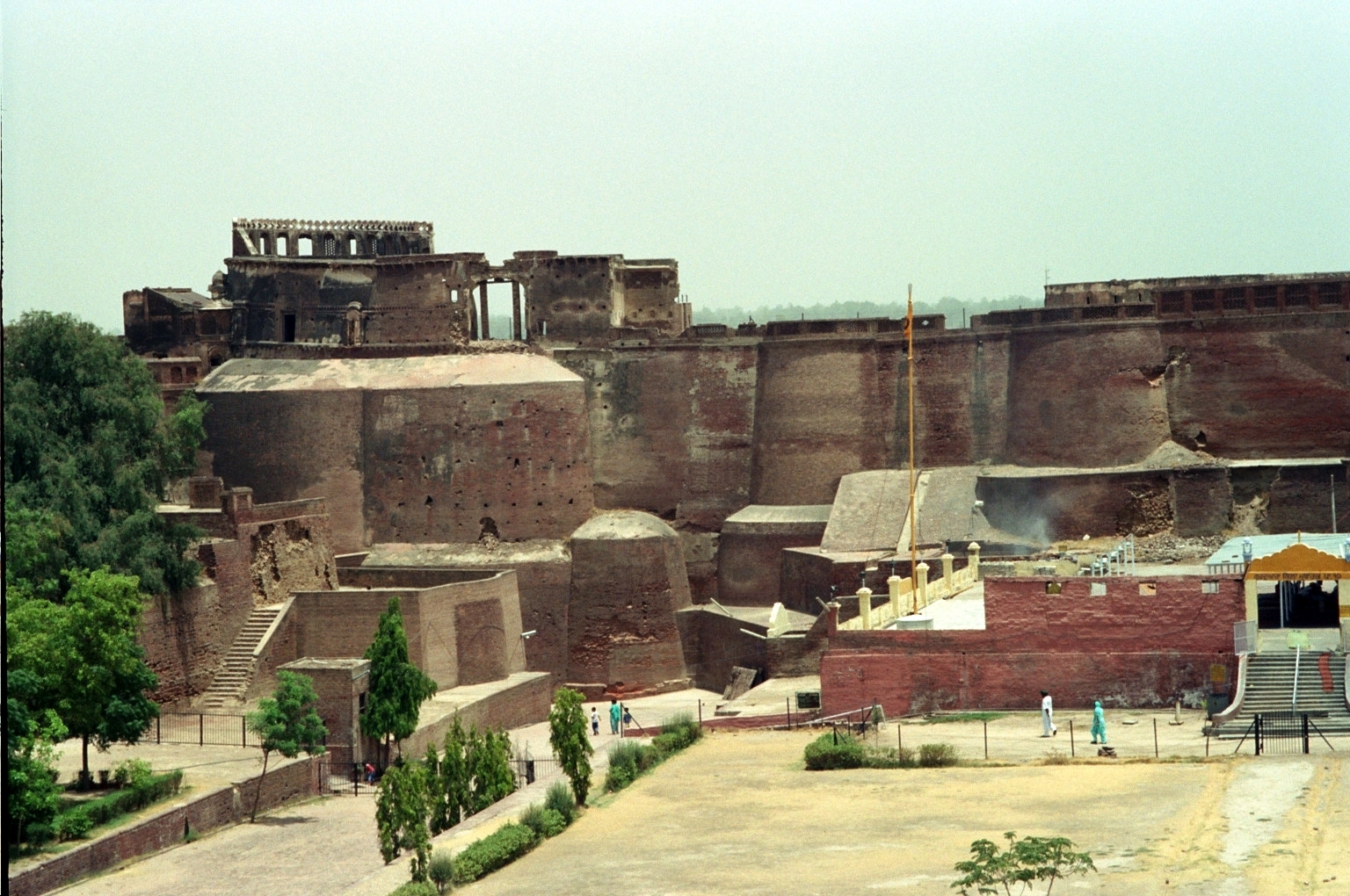

The Qila Mubarak fort at Bathinda, India was built by Kanishka the Great.

Kanishka the Great inaugurates Mahayana Buddhism. Illustration from 1910.
Art, Literature and Science

Around the beginning of the Common Era, perhaps coinciding with the development of Mahayana Buddhism, the distinctly realistic forms Greek sculpture and the tradition of depicting the Greek gods as human merged with the new Buddhist sensibilities to create the first image of Buddha, which looked remarkably like the Greek god Apollo.
Vatsayana’s famous Kama Sutra, or, Aphorisms of Love was written perhaps in the first or the second century AD.
References
1. Saka Rulers in India
2. Kushan empire TN class 6 – Indian Art and Culture for IAS Youtube
3. Indo-Greek Kingdom
